Arm Ethos-U Backend#
The Arm® Ethos™-U backend targets Edge/IoT-type AI use-cases by enabling optimal execution of quantized models on Arm® Ethos™-U55 NPU, Arm® Ethos™-U65 NPU, and Arm® Ethos™-U85 NPU, leveraging TOSA and the ethos-u-vela graph compiler. This document is a technical reference for using the Ethos-U backend, for a top level view with code examples please refer to the Arm Ethos-U Backend Tutorial.
Features#
Wide operator support for delegating large parts of models to highly optimized and low power Ethos-U NPUs.
A quantizer that optimizes quantization for the NPU target.
Example runtime integration for easy hardware bringup.
Target Requirements#
The target system must include an Ethos-U NPU.
Development Requirements#
Tip
All requirements can be downloaded using examples/arm/setup.sh --i-agree-to-the-contained-eula and added to the path using
set(CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX “${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}”)
source examples/arm/arm-scratch/setup_path.sh. Note that this means accepting the End-User License Agreements (EULA:s) required for using the downloaded software.
For the AOT flow, compilation of a model to .pte format using the Ethos-U backend, the requirements are:
TOSA Serialization Library for serializing the Exir IR graph into TOSA IR.
Ethos-U Vela graph compiler for compiling TOSA flatbuffers into an Ethos-U command stream.
And for building and running the example application available in examples/arm/executor_runner/:
Arm GNU Toolchain for cross compilation.
Arm® Corstone™ SSE-300 FVP for testing on a Arm® Cortex®-M55+Ethos-U55 reference design.
Arm® Corstone™ SSE-320 FVP for testing on a Arm® Cortex®-M85+Ethos-U85 reference design.
Fixed Virtual Platforms (FVPs) are freely available emulators provided by Arm for easy embedded development without the need for a physical development board.
Using the Arm Ethos-U Backend#
The main configuration point for the lowering is the EthosUCompileSpec consumed by the partitioner and quantizer.
The full user-facing API is documented below.
class EthosUCompileSpec(target: str, system_config: str | None = None, memory_mode: str | None = None, extra_flags: list[str] | None = None, config_ini: str | None = 'Arm/vela.ini')
Normalise Ethos-U compile configuration and compiler flags.
Args:
target (str): Ethos-U accelerator configuration (for example,
"ethos-u55-128").system_config (str | None): System configuration name from the Vela config file. Defaults based on
targetwhen omitted.memory_mode (str | None): Memory mode selection from the Vela config file. Defaults based on
targetwhen omitted.extra_flags (list[str] | None): Additional command-line flags for Vela.
config_ini (str | None): Path to a Vela .ini configuration file. Defaults to
"Arm/vela.ini".
def EthosUCompileSpec.dump_debug_info(self, debug_mode: executorch.backends.arm.common.arm_compile_spec.ArmCompileSpec.DebugMode | None):
Dump debugging information into the intermediates path.
Args:
debug_mode: The debug mode to use for dumping debug information.
def EthosUCompileSpec.dump_intermediate_artifacts_to(self, output_path: str | None):
Sets a path for dumping intermediate results during such as tosa and pte.
Args:
output_path: Path to dump intermediate results to.
def EthosUCompileSpec.get_intermediate_path(self) -> str | None:
Gets the path used for dumping intermediate results such as tosa and pte.
Returns: Path where intermediate results are saved.
def EthosUCompileSpec.get_output_format() -> str:
Return the artifact format emitted by this compile spec.
def EthosUCompileSpec.get_output_order_workaround(self) -> bool:
Gets whether the output order workaround is being applied.
def EthosUCompileSpec.get_pass_pipeline_config(self) -> executorch.backends.arm.common.pipeline_config.ArmPassPipelineConfig:
Returns configuration that controls how the Arm pass pipeline should behave. Subclasses may override to tweak defaults for specific targets.
def EthosUCompileSpec.set_output_order_workaround(self, output_order_workaround: bool):
Sets whether to apply the output order workaround.
Args:
output_order_workaround: Boolean indicating whether to apply the workaround.
def EthosUCompileSpec.set_pass_pipeline_config(self, config: executorch.backends.arm.common.pipeline_config.ArmPassPipelineConfig) -> None:
Sets the configuration that controls how the Arm pass pipeline should behave. Subclasses may override to tweak defaults for specific targets.
Args:
config: The custom ArmPassPipelineConfig to set.
Partitioner API#
See Partitioner API for more information of the Partitioner API.
Quantization#
Since the Ethos-U backend is integer-only, all operators intended be executed on the NPU needs to be quantized. The Ethos-U quantizer supports Post Training Quantization (PT2E) and Quantization-Aware Training (QAT) quantization.
For more information on quantization, see Quantization
Runtime Integration#
An example runtime application is available in examples/arm/executor_runner, and the steps requried for building and deploying it on a FVP it is explained in the previously mentioned Arm Ethos-U Backend Tutorial. The example application is recommended to use for testing basic functionality of your lowered models, as well as a starting point for developing runtime integrations for your own targets. For an in-depth explanation of the architecture of the executor_runner and the steps required for doing such an integration, please refer to Ethos-U porting guide.
Ethos-U memory modes#
The Ethos-U NPU provides two distinct memory interfaces:
One interface for low-latency, high-bandwidth memory.
On all Ethos-U NPUs(Ethos-U55, Ethos-U65, Ethos-U85), the low-latency memory is usually the SRAM of the SoC.
One interface for higher-latency, lower-bandwidth memory, typically external (off-chip) memory.
On a low-power microcontroller, the external memory is usually Flash.
On systems with Arm® Cortex™-A and a rich operating system, the external memory is typically DRAM.
When running an inference, the Ethos-U compiler and Ethos-U driver make use of three logical memory regions:
Ethos-U scratch buffer - a contiguous block of memory used by the NPU to store the intermediate tensors produced and consumed during inference.
Neural Network - a contiguous block of memory holding constant data such as weights, biases, quantization parameters required to run an inference.
Ethos-U fast scratch buffer - a contiguous block of memory, assumed to reside in on-chip memory in order to hide the higher latency/lower bandwidth of external memory. Only applicable for Ethos-U65 and Ethos-U85 on systems with Cortex-A and the external memory is assumed to be DRAM.
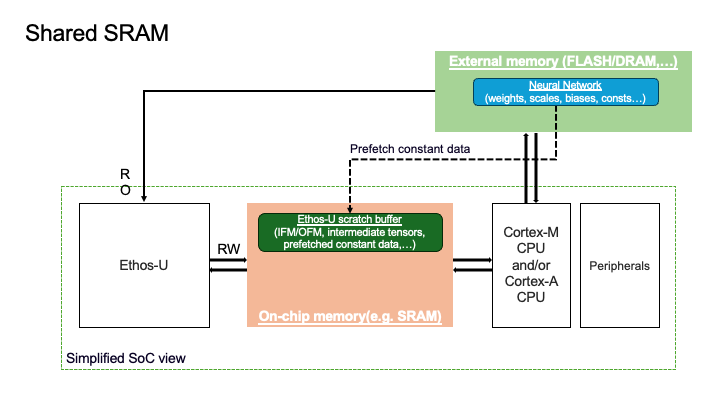
The placement of the scratch buffer and the Neural Network determine the memory mode to be used in the EthosUCompileSpec and when building the executor_runner. Three different memory modes are supported:
Memory Mode |
Ethos-U Scratch Buffer Placement |
Neural Network Placement |
When to Use |
Trade-off |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SRAM-Only |
On-chip SRAM |
On-chip SRAM |
When the ML model, the Ethos-U scratch buffer and the wider software stack fit within the SRAM of the SoC |
Limited by SRAM size; often not feasible for larger NNs |
Shared-SRAM |
On-chip SRAM |
External memory (Flash/DRAM) |
Most common mode on Cortex-M and Ethos-U systems; balances good performance and SRAM usage |
Requires enough SRAM to hold the largest intermediate tensor |
Dedicated-SRAM |
External memory |
External memory (Flash/DRAM) |
Most common mode for Cortex-A and Ethos-U systems. For very large models where the peak intermediates cannot fit in SRAM |
Need high-bandwidth external memory to deliver good performance |
Here is an in-depth explanation of the different modes:
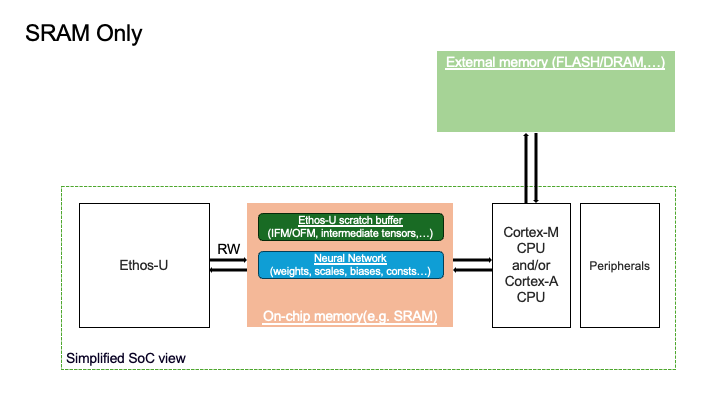
1. Sram-Only Memory Mode#
Ethos-U scratch buffer resides in the SRAM.
Neural Network resides in the SRAM.
Ethos-U fast scratch buffer is not used.
Characteristics:
Provides the best performance since all the memory traffic passes via the low-latency/high-bandwidth memory.
The performance uplift is especially noticeable on memory-bound workloads on the external interface.
Available on Ethos-U55, Ethos-U65 and Ethos-U85.
Limitations:
Embedded SoCs often have limited SRAM and NNs are becoming larger. This memory mode may be unsuitable for a system running a big model relative to the amount of SRAM available on the SoC. Below, you can see a visual representation of the placement of the two logical memory regions for the Sram Only configuration.
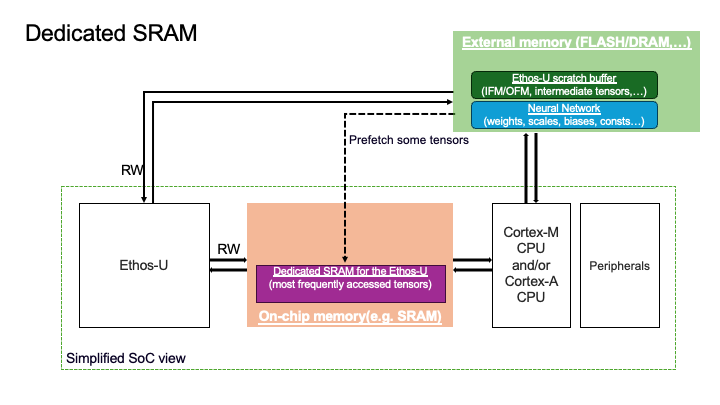
3. Dedicated-Sram Memory Mode#
Ethos-U scratch buffer resides in the External memory.
Neural Network resides in the External memory.
Ethos-U fast scratch buffer resides in the on-chip memory.
Characteristics:
Used when the peak intermediate tensor is too big to fit into the on-chip memory.
Enables silicon acceleration of large models.
The NPU stores the results from the intermediate computations in the external memory.
The dedicated SRAM acts as a software managed cache, improving performance by pre-fetching frequently accessed tensors to the on-chip memory.
Available on Ethos-U65 and Ethos-U85.
Limitations:
The SRAM space must be dedicated exculisely to the Ethos-U(the host processor should not access it).
Not available on Ethos-U55. Below, you can see a visual representation of the placement of the two logical memory regions for the Shared_Sram configuration.
The memory modes are defined within the vela.ini file. When you install ExecuTorch for the Ethos-U backend, you automatically install the compiler containing the vela.ini file so you can directly create a compile specification with these memory modes.
Reference#
→Partitioner API — Partitioner options.
→Quantization — Supported quantization schemes.
→Arm Ethos-U Troubleshooting — Troubleshooting and common issues.
→Arm Ethos-U Backend Tutorials — Tutorials.