torchaudio.prototype.functional.oscillator_bank¶
- torchaudio.prototype.functional.oscillator_bank(frequencies: Tensor, amplitudes: Tensor, sample_rate: float, reduction: str = 'sum', dtype: Optional[dtype] = torch.float64) Tensor[source]¶
DEPRECATED
Warning
This function has been deprecated. It will be removed from 2.9 release. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information.
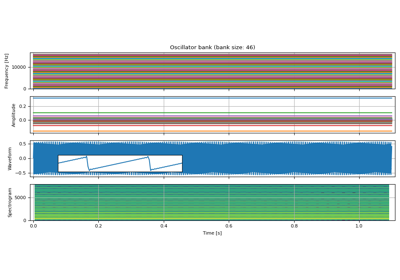
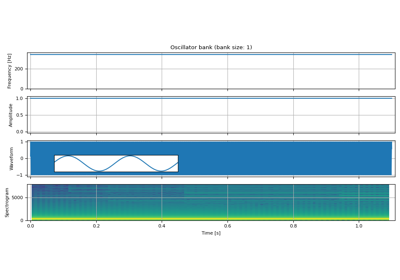
Synthesize waveform from the given instantaneous frequencies and amplitudes.
Note
The phase information of the output waveform is found by taking the cumulative sum of the given instantaneous frequencies (
frequencies). This incurs roundoff error when the data type does not have enough precision. Usingtorch.float64can work around this.The following figure shows the difference between
torch.float32andtorch.float64when generating a sin wave of constant frequency and amplitude with sample rate 8000 [Hz]. Notice thattorch.float32version shows artifacts that are not seen intorch.float64version.
- Parameters
frequencies (Tensor) – Sample-wise oscillator frequencies (Hz). Shape (…, time, N).
amplitudes (Tensor) – Sample-wise oscillator amplitude. Shape: (…, time, N).
sample_rate (float) – Sample rate
reduction (str) – Reduction to perform. Valid values are
"sum","mean"or"none". Default:"sum"dtype (torch.dpython:type or None, optional) – The data type on which cumulative sum operation is performed. Default:
torch.float64. PassNoneto disable the casting.
- Returns
The resulting waveform.
If
reductionis"none", then the shape is (…, time, N), otherwise the shape is (…, time).- Return type
Tensor
- Tutorials using
oscillator_bank: