Note
Click here to download the full example code
Speech Enhancement with MVDR Beamforming¶
Author: Zhaoheng Ni
1. Overview¶
This is a tutorial on applying Minimum Variance Distortionless Response (MVDR) beamforming to estimate enhanced speech with TorchAudio.
Steps:
Generate an ideal ratio mask (IRM) by dividing the clean/noise magnitude by the mixture magnitude.
Estimate power spectral density (PSD) matrices using
torchaudio.transforms.PSD().Estimate enhanced speech using MVDR modules (
torchaudio.transforms.SoudenMVDR()andtorchaudio.transforms.RTFMVDR()).Benchmark the two methods (
torchaudio.functional.rtf_evd()andtorchaudio.functional.rtf_power()) for computing the relative transfer function (RTF) matrix of the reference microphone.
import torch
import torchaudio
import torchaudio.functional as F
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mir_eval
from IPython.display import Audio
2.8.0+cu126
2.8.0
2. Preparation¶
2.1. Import the packages¶
First, we install and import the necessary packages.
mir_eval, pesq, and pystoi packages are required for
evaluating the speech enhancement performance.
# When running this example in notebook, install the following packages.
# !pip3 install mir_eval
# !pip3 install pesq
# !pip3 install pystoi
from pesq import pesq
from pystoi import stoi
from torchaudio.utils import download_asset
2.2. Download audio data¶
The multi-channel audio example is selected from ConferencingSpeech dataset.
The original filename is
SSB07200001\#noise-sound-bible-0038\#7.86_6.16_3.00_3.14_4.84_134.5285_191.7899_0.4735\#15217\#25.16333303751458\#0.2101221178590021.wav
which was generated with:
SSB07200001.wavfrom AISHELL-3 (Apache License v.2.0)noise-sound-bible-0038.wavfrom MUSAN (Attribution 4.0 International — CC BY 4.0)
SAMPLE_RATE = 16000
SAMPLE_CLEAN = download_asset("tutorial-assets/mvdr/clean_speech.wav")
SAMPLE_NOISE = download_asset("tutorial-assets/mvdr/noise.wav")
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/mvdr_tutorial.py:91: UserWarning: torchaudio.utils.download.download_asset has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
SAMPLE_CLEAN = download_asset("tutorial-assets/mvdr/clean_speech.wav")
0%| | 0.00/0.98M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
100%|##########| 0.98M/0.98M [00:00<00:00, 236MB/s]
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/mvdr_tutorial.py:92: UserWarning: torchaudio.utils.download.download_asset has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
SAMPLE_NOISE = download_asset("tutorial-assets/mvdr/noise.wav")
0%| | 0.00/1.95M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
100%|##########| 1.95M/1.95M [00:00<00:00, 230MB/s]
2.3. Helper functions¶
def plot_spectrogram(stft, title="Spectrogram"):
magnitude = stft.abs()
spectrogram = 20 * torch.log10(magnitude + 1e-8).numpy()
figure, axis = plt.subplots(1, 1)
img = axis.imshow(spectrogram, cmap="viridis", vmin=-100, vmax=0, origin="lower", aspect="auto")
axis.set_title(title)
plt.colorbar(img, ax=axis)
def plot_mask(mask, title="Mask"):
mask = mask.numpy()
figure, axis = plt.subplots(1, 1)
img = axis.imshow(mask, cmap="viridis", origin="lower", aspect="auto")
axis.set_title(title)
plt.colorbar(img, ax=axis)
def si_snr(estimate, reference, epsilon=1e-8):
estimate = estimate - estimate.mean()
reference = reference - reference.mean()
reference_pow = reference.pow(2).mean(axis=1, keepdim=True)
mix_pow = (estimate * reference).mean(axis=1, keepdim=True)
scale = mix_pow / (reference_pow + epsilon)
reference = scale * reference
error = estimate - reference
reference_pow = reference.pow(2)
error_pow = error.pow(2)
reference_pow = reference_pow.mean(axis=1)
error_pow = error_pow.mean(axis=1)
si_snr = 10 * torch.log10(reference_pow) - 10 * torch.log10(error_pow)
return si_snr.item()
def generate_mixture(waveform_clean, waveform_noise, target_snr):
power_clean_signal = waveform_clean.pow(2).mean()
power_noise_signal = waveform_noise.pow(2).mean()
current_snr = 10 * torch.log10(power_clean_signal / power_noise_signal)
waveform_noise *= 10 ** (-(target_snr - current_snr) / 20)
return waveform_clean + waveform_noise
def evaluate(estimate, reference):
si_snr_score = si_snr(estimate, reference)
(
sdr,
_,
_,
_,
) = mir_eval.separation.bss_eval_sources(reference.numpy(), estimate.numpy(), False)
pesq_mix = pesq(SAMPLE_RATE, estimate[0].numpy(), reference[0].numpy(), "wb")
stoi_mix = stoi(reference[0].numpy(), estimate[0].numpy(), SAMPLE_RATE, extended=False)
print(f"SDR score: {sdr[0]}")
print(f"Si-SNR score: {si_snr_score}")
print(f"PESQ score: {pesq_mix}")
print(f"STOI score: {stoi_mix}")
3. Generate Ideal Ratio Masks (IRMs)¶
3.1. Load audio data¶
waveform_clean, sr = torchaudio.load(SAMPLE_CLEAN)
waveform_noise, sr2 = torchaudio.load(SAMPLE_NOISE)
assert sr == sr2 == SAMPLE_RATE
# The mixture waveform is a combination of clean and noise waveforms with a desired SNR.
target_snr = 3
waveform_mix = generate_mixture(waveform_clean, waveform_noise, target_snr)
/pytorch/audio/src/torchaudio/_backend/utils.py:213: UserWarning: In 2.9, this function's implementation will be changed to use torchaudio.load_with_torchcodec` under the hood. Some parameters like ``normalize``, ``format``, ``buffer_size``, and ``backend`` will be ignored. We recommend that you port your code to rely directly on TorchCodec's decoder instead: https://docs.pytorch.org/torchcodec/stable/generated/torchcodec.decoders.AudioDecoder.html#torchcodec.decoders.AudioDecoder.
warnings.warn(
/pytorch/audio/src/torchaudio/_backend/ffmpeg.py:88: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = torchaudio.io.StreamReader(src, format, None, buffer_size)
Note: To improve computational robustness, it is recommended to represent
the waveforms as double-precision floating point (torch.float64 or torch.double) values.
3.2. Compute STFT coefficients¶
N_FFT = 1024
N_HOP = 256
stft = torchaudio.transforms.Spectrogram(
n_fft=N_FFT,
hop_length=N_HOP,
power=None,
)
istft = torchaudio.transforms.InverseSpectrogram(n_fft=N_FFT, hop_length=N_HOP)
stft_mix = stft(waveform_mix)
stft_clean = stft(waveform_clean)
stft_noise = stft(waveform_noise)
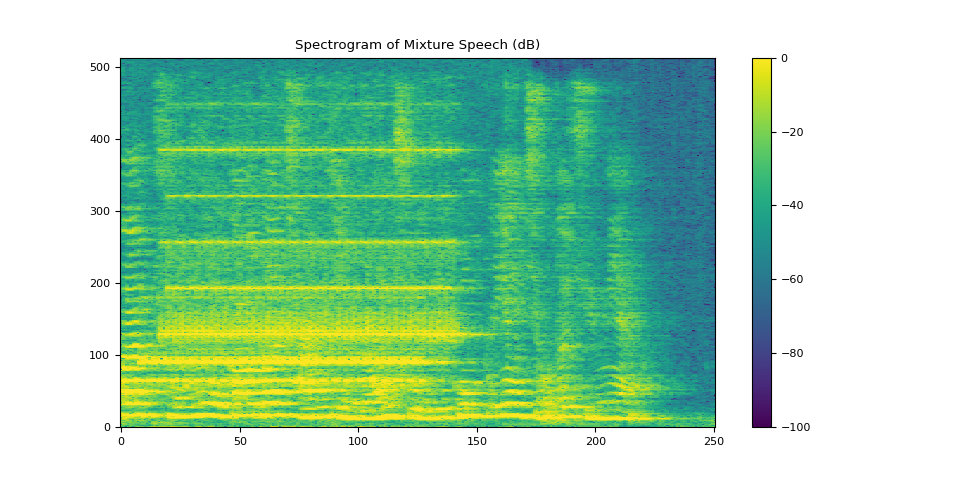
3.2.1. Visualize mixture speech¶
We evaluate the quality of the mixture speech or the enhanced speech using the following three metrics:
signal-to-distortion ratio (SDR)
scale-invariant signal-to-noise ratio (Si-SNR, or Si-SDR in some papers)
Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ)
We also evaluate the intelligibility of the speech with the Short-Time Objective Intelligibility (STOI) metric.
plot_spectrogram(stft_mix[0], "Spectrogram of Mixture Speech (dB)")
evaluate(waveform_mix[0:1], waveform_clean[0:1])
Audio(waveform_mix[0], rate=SAMPLE_RATE)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/mvdr_tutorial.py:153: FutureWarning: mir_eval.separation.bss_eval_sources
Deprecated as of mir_eval version 0.8.
It will be removed in mir_eval version 0.9.
) = mir_eval.separation.bss_eval_sources(reference.numpy(), estimate.numpy(), False)
SDR score: 4.14036218177802
Si-SNR score: 4.104058905536078
PESQ score: 2.0084526538848877
STOI score: 0.7724339398714715
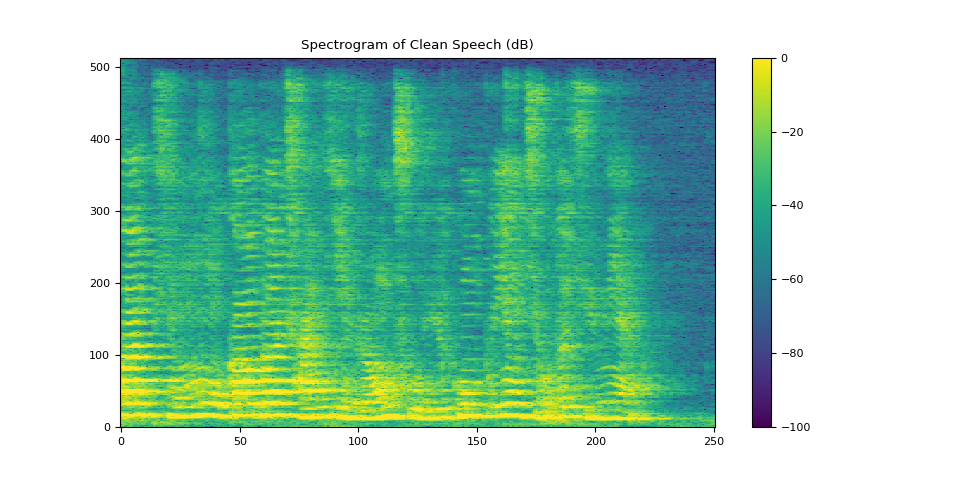
3.2.2. Visualize clean speech¶
plot_spectrogram(stft_clean[0], "Spectrogram of Clean Speech (dB)")
Audio(waveform_clean[0], rate=SAMPLE_RATE)
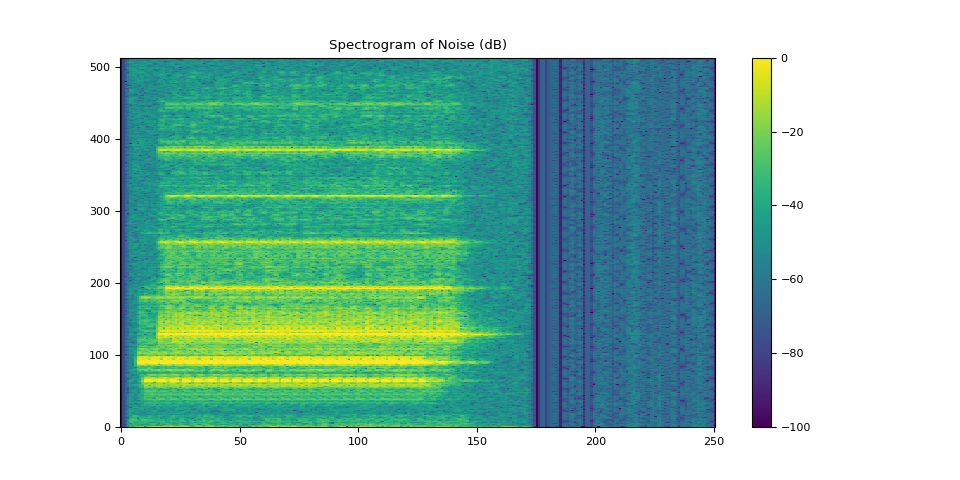
3.2.3. Visualize noise¶
plot_spectrogram(stft_noise[0], "Spectrogram of Noise (dB)")
Audio(waveform_noise[0], rate=SAMPLE_RATE)
3.3. Define the reference microphone¶
We choose the first microphone in the array as the reference channel for demonstration. The selection of the reference channel may depend on the design of the microphone array.
You can also apply an end-to-end neural network which estimates both the reference channel and the PSD matrices, then obtains the enhanced STFT coefficients by the MVDR module.
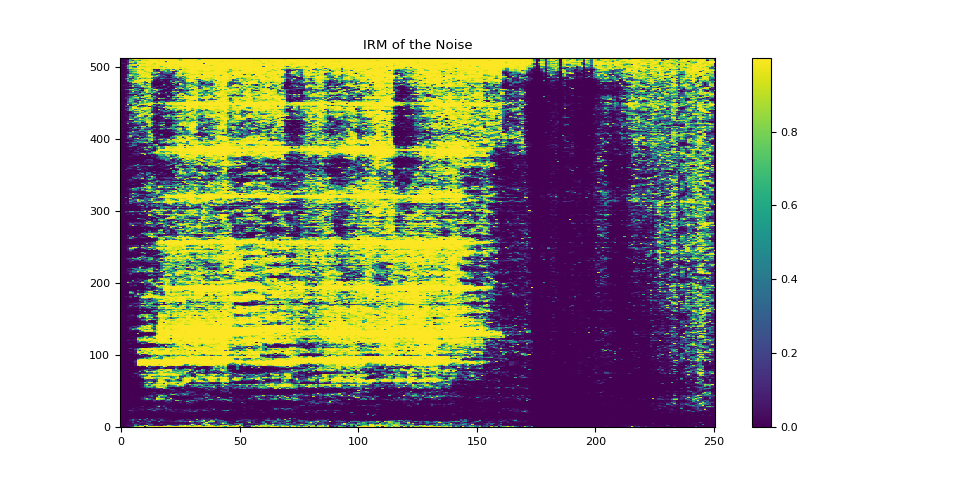
3.4. Compute IRMs¶
def get_irms(stft_clean, stft_noise):
mag_clean = stft_clean.abs() ** 2
mag_noise = stft_noise.abs() ** 2
irm_speech = mag_clean / (mag_clean + mag_noise)
irm_noise = mag_noise / (mag_clean + mag_noise)
return irm_speech[REFERENCE_CHANNEL], irm_noise[REFERENCE_CHANNEL]
irm_speech, irm_noise = get_irms(stft_clean, stft_noise)
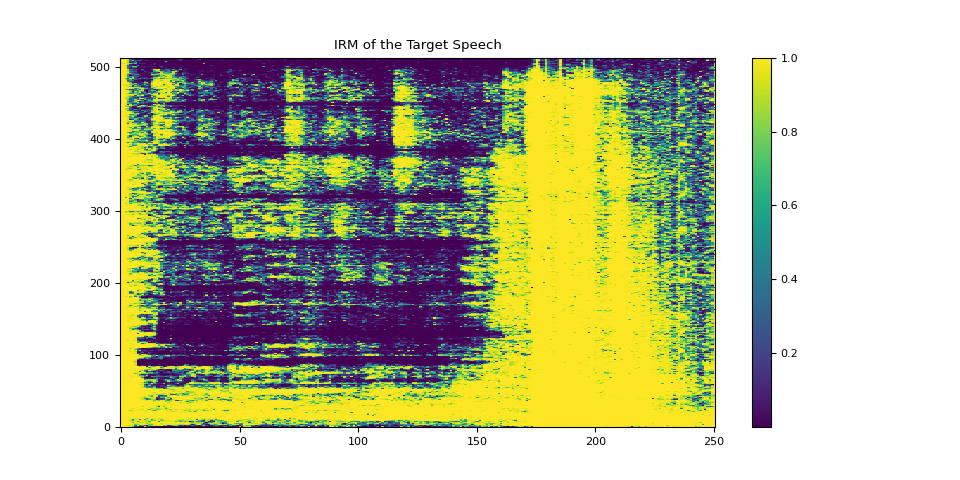
3.4.1. Visualize IRM of target speech¶
plot_mask(irm_speech, "IRM of the Target Speech")
3.4.2. Visualize IRM of noise¶
plot_mask(irm_noise, "IRM of the Noise")
4. Compute PSD matrices¶
torchaudio.transforms.PSD() computes the time-invariant PSD matrix given
the multi-channel complex-valued STFT coefficients of the mixture speech
and the time-frequency mask.
The shape of the PSD matrix is (…, freq, channel, channel).
psd_transform = torchaudio.transforms.PSD()
psd_speech = psd_transform(stft_mix, irm_speech)
psd_noise = psd_transform(stft_mix, irm_noise)
5. Beamforming using SoudenMVDR¶
5.1. Apply beamforming¶
torchaudio.transforms.SoudenMVDR() takes the multi-channel
complexed-valued STFT coefficients of the mixture speech, PSD matrices of
target speech and noise, and the reference channel inputs.
The output is a single-channel complex-valued STFT coefficients of the enhanced speech.
We can then obtain the enhanced waveform by passing this output to the
torchaudio.transforms.InverseSpectrogram() module.
mvdr_transform = torchaudio.transforms.SoudenMVDR()
stft_souden = mvdr_transform(stft_mix, psd_speech, psd_noise, reference_channel=REFERENCE_CHANNEL)
waveform_souden = istft(stft_souden, length=waveform_mix.shape[-1])
5.2. Result for SoudenMVDR¶
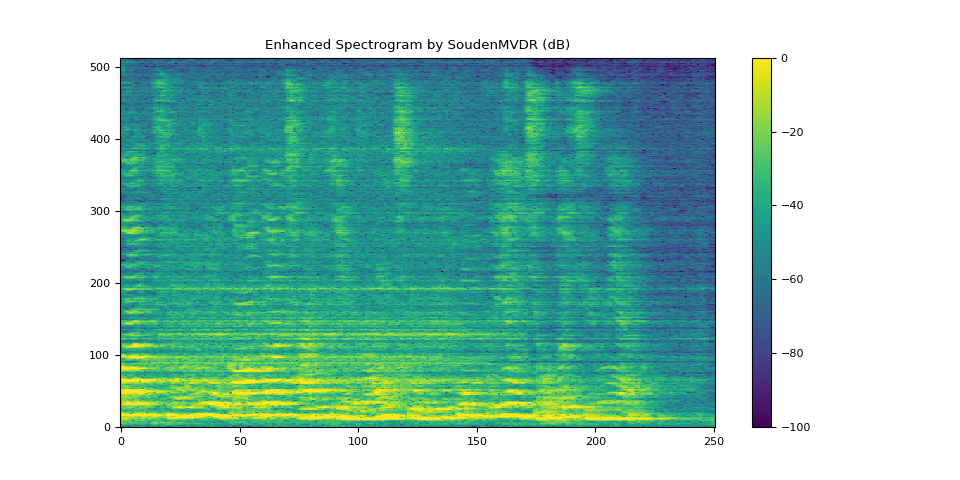
plot_spectrogram(stft_souden, "Enhanced Spectrogram by SoudenMVDR (dB)")
waveform_souden = waveform_souden.reshape(1, -1)
evaluate(waveform_souden, waveform_clean[0:1])
Audio(waveform_souden, rate=SAMPLE_RATE)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/mvdr_tutorial.py:153: FutureWarning: mir_eval.separation.bss_eval_sources
Deprecated as of mir_eval version 0.8.
It will be removed in mir_eval version 0.9.
) = mir_eval.separation.bss_eval_sources(reference.numpy(), estimate.numpy(), False)
SDR score: 17.94623444750873
Si-SNR score: 12.21520261226658
PESQ score: 3.3447437286376953
STOI score: 0.8712864479161742
6. Beamforming using RTFMVDR¶
6.1. Compute RTF¶
TorchAudio offers two methods for computing the RTF matrix of a target speech:
torchaudio.functional.rtf_evd(), which applies eigenvalue decomposition to the PSD matrix of target speech to get the RTF matrix.torchaudio.functional.rtf_power(), which applies the power iteration method. You can specify the number of iterations with argumentn_iter.
rtf_evd = F.rtf_evd(psd_speech)
rtf_power = F.rtf_power(psd_speech, psd_noise, reference_channel=REFERENCE_CHANNEL)
6.2. Apply beamforming¶
torchaudio.transforms.RTFMVDR() takes the multi-channel
complexed-valued STFT coefficients of the mixture speech, RTF matrix of target speech,
PSD matrix of noise, and the reference channel inputs.
The output is a single-channel complex-valued STFT coefficients of the enhanced speech.
We can then obtain the enhanced waveform by passing this output to the
torchaudio.transforms.InverseSpectrogram() module.
mvdr_transform = torchaudio.transforms.RTFMVDR()
# compute the enhanced speech based on F.rtf_evd
stft_rtf_evd = mvdr_transform(stft_mix, rtf_evd, psd_noise, reference_channel=REFERENCE_CHANNEL)
waveform_rtf_evd = istft(stft_rtf_evd, length=waveform_mix.shape[-1])
# compute the enhanced speech based on F.rtf_power
stft_rtf_power = mvdr_transform(stft_mix, rtf_power, psd_noise, reference_channel=REFERENCE_CHANNEL)
waveform_rtf_power = istft(stft_rtf_power, length=waveform_mix.shape[-1])
6.3. Result for RTFMVDR with rtf_evd¶
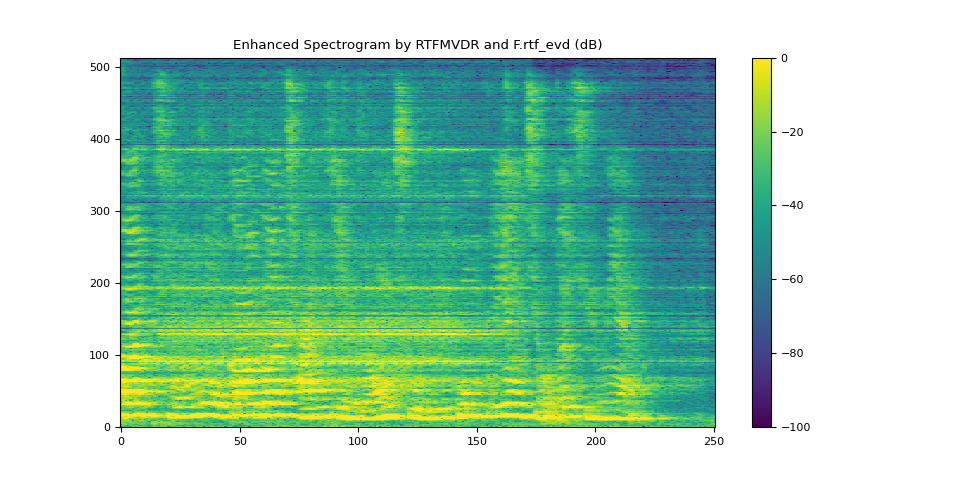
plot_spectrogram(stft_rtf_evd, "Enhanced Spectrogram by RTFMVDR and F.rtf_evd (dB)")
waveform_rtf_evd = waveform_rtf_evd.reshape(1, -1)
evaluate(waveform_rtf_evd, waveform_clean[0:1])
Audio(waveform_rtf_evd, rate=SAMPLE_RATE)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/mvdr_tutorial.py:153: FutureWarning: mir_eval.separation.bss_eval_sources
Deprecated as of mir_eval version 0.8.
It will be removed in mir_eval version 0.9.
) = mir_eval.separation.bss_eval_sources(reference.numpy(), estimate.numpy(), False)
SDR score: 11.880210635280285
Si-SNR score: 10.714419996128075
PESQ score: 3.083890914916992
STOI score: 0.8261544910053076
6.4. Result for RTFMVDR with rtf_power¶
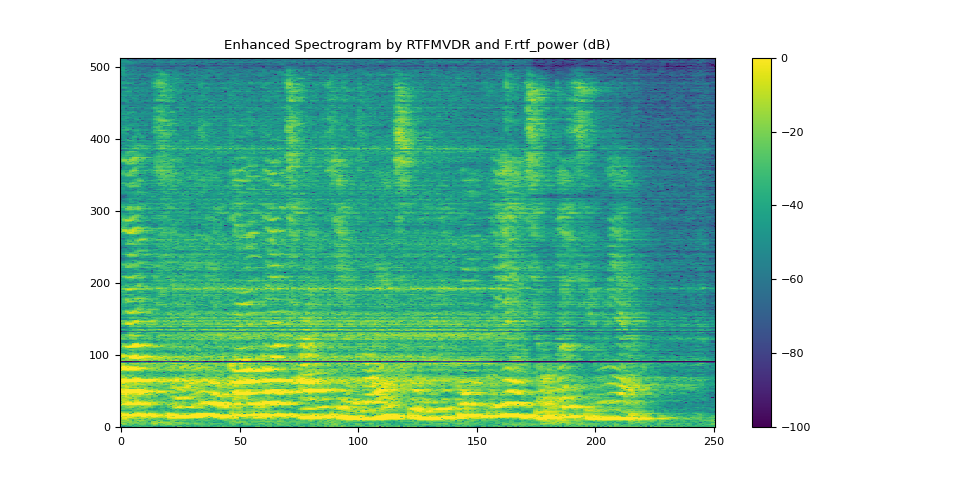
plot_spectrogram(stft_rtf_power, "Enhanced Spectrogram by RTFMVDR and F.rtf_power (dB)")
waveform_rtf_power = waveform_rtf_power.reshape(1, -1)
evaluate(waveform_rtf_power, waveform_clean[0:1])
Audio(waveform_rtf_power, rate=SAMPLE_RATE)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/mvdr_tutorial.py:153: FutureWarning: mir_eval.separation.bss_eval_sources
Deprecated as of mir_eval version 0.8.
It will be removed in mir_eval version 0.9.
) = mir_eval.separation.bss_eval_sources(reference.numpy(), estimate.numpy(), False)
SDR score: 15.42459027693396
Si-SNR score: 13.035440892133302
PESQ score: 3.487997531890869
STOI score: 0.8798278461896831
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.851 seconds)



