VideoDecoder¶
- class torchcodec.decoders.VideoDecoder(source: Union[str, Path, RawIOBase, BufferedReader, bytes, Tensor], *, stream_index: Optional[int] = None, dimension_order: Literal['NCHW', 'NHWC'] = 'NCHW', num_ffmpeg_threads: int = 1, device: Optional[Union[str, device]] = 'cpu', seek_mode: Literal['exact', 'approximate'] = 'exact')[source]¶
A single-stream video decoder.
- Parameters:
source (str,
Pathlib.path, bytes,torch.Tensoror file-like object) –The source of the video:
If
str: a local path or a URL to a video file.If
Pathlib.path: a path to a local video file.If
bytesobject ortorch.Tensor: the raw encoded video data.If file-like object: we read video data from the object on demand. The object must expose the methods read(self, size: int) -> bytes and seek(self, offset: int, whence: int) -> bytes. Read more in: Streaming data through file-like support.
stream_index (int, optional) – Specifies which stream in the video to decode frames from. Note that this index is absolute across all media types. If left unspecified, then the best stream is used.
dimension_order (str, optional) –
The dimension order of the decoded frames. This can be either “NCHW” (default) or “NHWC”, where N is the batch size, C is the number of channels, H is the height, and W is the width of the frames. .. note:
Frames are natively decoded in NHWC format by the underlying FFmpeg implementation. Converting those into NCHW format is a cheap no-copy operation that allows these frames to be transformed using the `torchvision transforms <https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html>`_.
num_ffmpeg_threads (int, optional) – The number of threads to use for decoding. Use 1 for single-threaded decoding which may be best if you are running multiple instances of
VideoDecoderin parallel. Use a higher number for multi-threaded decoding which is best if you are running a single instance ofVideoDecoder. Passing 0 lets FFmpeg decide on the number of threads. Default: 1.device (str or torch.device, optional) – The device to use for decoding. Default: “cpu”.
seek_mode (str, optional) – Determines if frame access will be “exact” or “approximate”. Exact guarantees that requesting frame i will always return frame i, but doing so requires an initial scan of the file. Approximate is faster as it avoids scanning the file, but less accurate as it uses the file’s metadata to calculate where i probably is. Default: “exact”. Read more about this parameter in: Exact vs Approximate seek mode: Performance and accuracy comparison
- Variables:
metadata (VideoStreamMetadata) – Metadata of the video stream.
stream_index (int) – The stream index that this decoder is retrieving frames from. If a stream index was provided at initialization, this is the same value. If it was left unspecified, this is the best stream.
Examples using
VideoDecoder:
Exact vs Approximate seek mode: Performance and accuracy comparison
Exact vs Approximate seek mode: Performance and accuracy comparison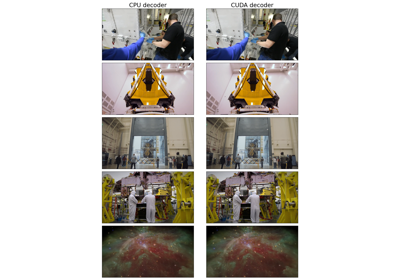
Accelerated video decoding on GPUs with CUDA and NVDEC
Accelerated video decoding on GPUs with CUDA and NVDEC- __getitem__(key: Union[Integral, slice]) Tensor[source]¶
Return frame or frames as tensors, at the given index or range.
Note
If you need to decode multiple frames, we recommend using the batch methods instead, since they are faster:
get_frames_at(),get_frames_in_range(),get_frames_played_at(), andget_frames_played_in_range().
- get_frame_at(index: int) Frame[source]¶
Return a single frame at the given index.
Note
If you need to decode multiple frames, we recommend using the batch methods instead, since they are faster:
get_frames_at(),get_frames_in_range(),get_frames_played_at(),get_frames_played_in_range().
- get_frame_played_at(seconds: float) Frame[source]¶
Return a single frame played at the given timestamp in seconds.
Note
If you need to decode multiple frames, we recommend using the batch methods instead, since they are faster:
get_frames_at(),get_frames_in_range(),get_frames_played_at(),get_frames_played_in_range().
- get_frames_at(indices: list[int]) FrameBatch[source]¶
Return frames at the given indices.
- Parameters:
indices (list of int) – The indices of the frames to retrieve.
- Returns:
The frames at the given indices.
- Return type:
- get_frames_in_range(start: int, stop: int, step: int = 1) FrameBatch[source]¶
Return multiple frames at the given index range.
Frames are in [start, stop).
- Parameters:
- Returns:
The frames within the specified range.
- Return type:
- get_frames_played_at(seconds: list[float]) FrameBatch[source]¶
Return frames played at the given timestamps in seconds.
- Parameters:
seconds (list of float) – The timestamps in seconds when the frames are played.
- Returns:
The frames that are played at
seconds.- Return type:
- get_frames_played_in_range(start_seconds: float, stop_seconds: float) FrameBatch[source]¶
Returns multiple frames in the given range.
Frames are in the half open range [start_seconds, stop_seconds). Each returned frame’s pts, in seconds, is inside of the half open range.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
The frames within the specified range.
- Return type: